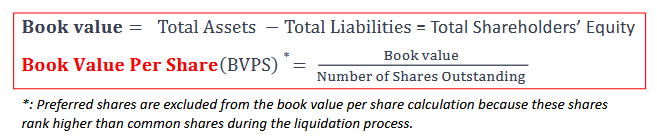Stock valuation: An Introduction
Stock valuation is the process of estimating the intrinsic value of a stock, also known as its fundamental value. This intrinsic value represents the true worth of a stock based on financial and economic data, helping investors make informed decisions about whether to buy, hold, or sell a stock.
The primary goal of stock valuation is to provide analysts and investors with the tools to determine whether a stock is undervalued, fairly valued, or overvalued in the market. Ultimately, this guides investment decisions and portfolio management strategies.
Stock valuation combines both art and science. It involves a mix of financial models, economic analysis, and sometimes subjective judgment. While accounting data is one source for valuation, there are several financial methods that offer unique perspectives and calculations.
Stock valuation: 2 Methods
Method 1: Book Value per Share (BVPS):
• BVPS represents the net asset value per share of a company, calculated by dividing total book value (assets minus liabilities) by the number of outstanding shares. It provides an estimate of the intrinsic value of a company's stock based on its net assets.
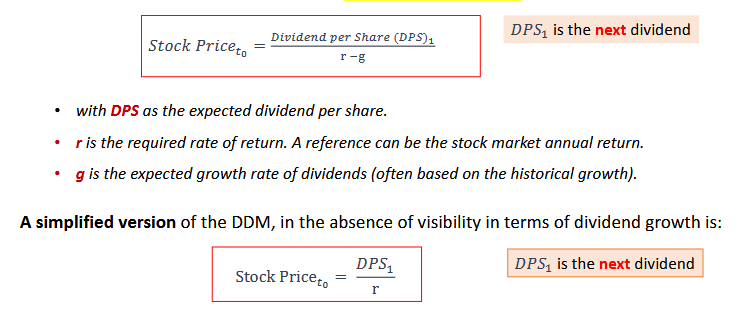
Method 2: Dividend Discount Model (DDM):
• This model focuses on the present value of future dividends expected from a stock.
• Assumes that a stock’s value is equal to the discounted sum of all future dividend payments.
What does accounting tell us? The book value is a financial metric that represents the net asset value of the company as recorded on its balance sheet. It is a fundamental measure used to assess the intrinsic value of a company's equity.
Many famous investors, including billionaire Warren Buffett, built their portfolios of investments and their fortunes in part by buying stocks with market valuations below their book valuations.
The market value is the market capitalization:
𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐂𝐚𝐩𝐢𝐭𝐚𝐥𝐢𝐳𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 = Share Price x Number of Outstanding Shares
The DDM is used to value stocks that pay dividends. It calculates the present value of expected future dividend payments.
The basic formula for DDM, based on the Gordon Growth Model, is: