Tourism industry is important for the benefits it brings and due to its role as a commercial activity that creates demand and growth for many more industries. Tourism not only contributes towards more economic activities but also generates more employment, revenues and play a significant role in development thus its impact on the gross domestic product of any country.
Introduction to Tourism
To remember :
UNWTO: The United World Tourism Organisation is an international organisation that is responsible for the
implementation and promotion of sustainable and responsible tourism practices.
Definitions
Description of Tourism
- The movement of people
- Travelling away from usual surrounding
- Temporary or short-term travel
- The purpose of the journey is not for employment or permanent residence
- The implication of tourism as an experience
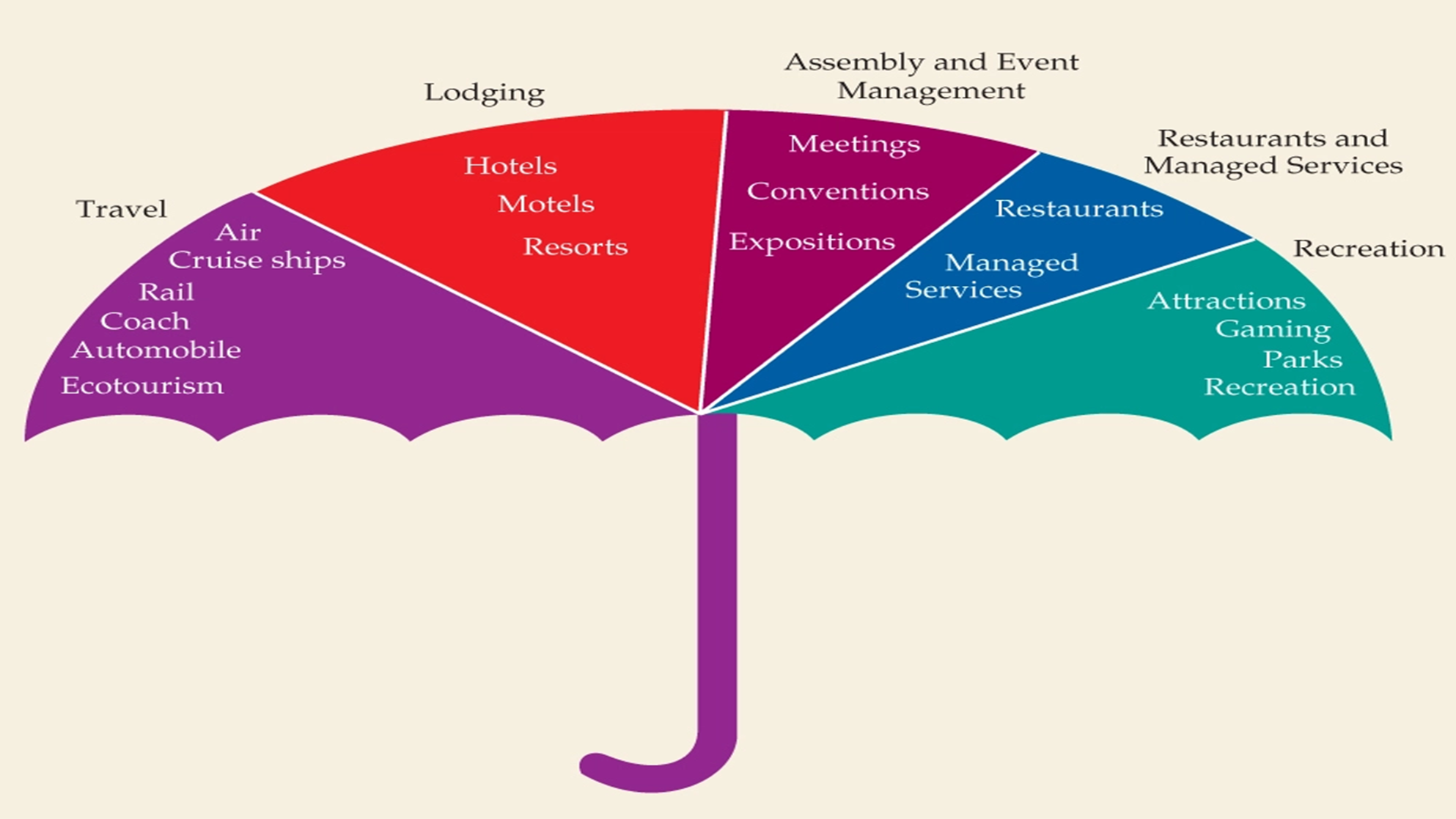
Primary Industries Involved in Tourism
Definitions
Description of a Tourist
- Reasons for travelling
- Length of stay
- Group size
- Place of origin
- Method of travelling
Definitions
Categorisations of Travellers
Tourist Factors
Temporal - the length of stay
Spatial - travelling to different places - the distance of travelling
The Purpose of the Journey - why are you travelling
Temporal
- stay-overs
- stop-overs
- excursionists
Spatial
- Domestic - takes place when people travel within the borders of the country in which they reside. All tourists travelling within the borders of a
- country for the purpose of business or leisure, who spend money while travelling and stay for more than 24 hours but less than a year.
- International - takes place when people travel outside the borders of their country of residence
- In-bound - someone who lives in one country and enters another country for tourism purposes
- Outbound - someone who leaves their country of origin to visit a different country for tourism purposes
The Purpose of the Journey
- Leisure - free time you have
- Recreation - activities done during leisure
- Personal Reasons - family and friends
- Business Reasons - "MICE"
The Nature of Tourism
Service-Based Industry
- A dynamic sector that can be described in terms of supply and demand
- Supply includes all facilities, programmes, attractions, and land uses designed & managed for the visitors
- Tourists that form core generating markets are identified as the demand side
- Tourism relies heavily on the demand of its tourists = demand dictates supply
To remember :
Tourist = demand
Attraction and Facilities = supply
- you have to adapt to meet the needs of the tourist
Tourism Supply
Tourism Supply = the provision of variety of tourism products (goods and services) to tourists and consumers at a particular market or destination in a given time. It also refers to variety of supply channels. These channels may be wholesale, retail on the basis of distribution. These may also be direct or indirect channels on the basis of interaction between the seller and buyer. Tourism supply can also be online and offline depending upon the mode of purchase of tourism product
Characteristics of Tourism Supply
- Tourism supply depends upon provision of variety of tourism products in a particular market.
- Tourism supply is directly related to tourism demand.
- Tourism supply is generally continuous except upon certain situations like global lockdowns and administrative failures of countries across the world.
- Tourism supply varies across different markets.
- Tourism supply is flexible. Tourism supply is sensitive to different internal and external factors.
- Tourism supply varies due to numerous dependent and independent variables.
- Tourism supply depends upon numerous factors i.e. geographical, climatic, seasonal, political, and international factors.
Tourism Demand
Tourism Demand = the requirement of variety of tourism products (Goods and Services) at a particular place or market in a given time on a given price, therefore it is the requirements of tourism products
Characteristics of Tourism Demand
- Tourism demand depends on a variety of tourism products in a particular market.
- Tourism demand depends upon the supply of tourism products.
- Tourism demand is generally continuous except in certain situations like global lockdowns and administrative failures of countries across the world.
- Tourism demand varies in different markets.
- Tourism demand is flexible.
- Tourism demand is sensitive to different internal and external factors.
- Tourism demand exhibits variations due to numerous dependent and independent variables.
- Tourism demand depends upon numerous factors, including socio-cultural, psychological, geographical, climatic, seasonal, political, and international factors.
Tourism Leisure and Recreation
Leisure = free time, a time in which we have no deadlines to follow, no goals to chase. Leisure is an experience.
Free time is time spent away from the business, work, job hunting, domestic chores and education. It also excludes time spent on necessary activities such as eating and sleeping. From a research perspective, this approach has the advantages of being quantifiable and comparable over time and place. Leisure as an experience usually emphasizes dimensions of perceived freedom and choice.
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. It is the activities that happen during an individuals’ leisure time. Recreation may be active or passive and take place inside or outside the home.
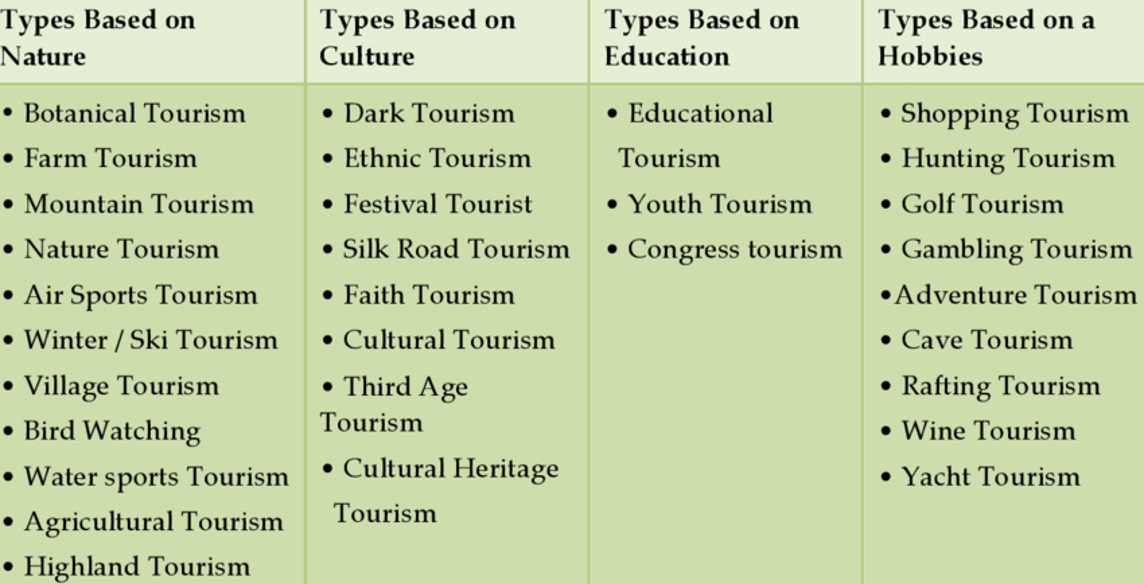
Types of Tourism
To remember :
Leisure
Business
Edutourism
Religious
Sports
Leisure Tourism: Leisure is time left over to spend freely, after the basic needs of eating, sleeping and other necessities have been met. Recreation is an activity done for enjoyment when one is not working
Business Tourism: a result of an employee being sent to a destination other than their usual work environment, with a specific goal in mind, but with the freedom to explore during their leisure time. Business tourism consists of MICE. At the end of the business trip, a specific goal, or set of goals, should have been achieved in relation to the business.
To remember :
- Meetings: share and exchange knowledge and ideas on a specific concept or topic
- Incentives: hosted for a select group of employees who have exceeded the goals or performance quotas
- Conventions: where delegates discuss a certain topic in an industry while participating in activities. Delegates are usually able to deliver a presentation on new ideas or recent findings in a specific industry
- Exhibitions: products and services are displayed to the public at a specific venue
Edutourism: learning something about the destination, attraction or activity that they did not previously know. This information is communicated to them by the guides or interpreters and will focus on a specific topic. Educational tourism takes place in various forms (historical attractions, sightseeing, wildlife tourism, adventure tourism, ecotourism). Guides will communicate facts and anecdotes to the visitors as a means of exchanging knowledge.
Education = the process of exchanging knowledge, from an expert to a student or tourists.
To remember :
For an activity to be classified as educational, the following should be identified:
- A message of welcoming
- General information should be provided to guide tourists safely and quickly
- Information on alternative routes and/ or attractions, in order to direct visitor flows
- Information on queuing times, to facilitate better planning
- Educational information on the natural, cultural and historical features of the area
- Information on the appropriate visitor in the area
Religious/ Faith Tourism: where individuals or groups of people travel, for the purpose of religious practices. A pilgrimage is a journey undertaken by an individual or a group of people, to a sacred destination
Sports Tourism: Leisure-based travel that takes individuals outside of their home communities to participate in physical activities (active sports tourism), to watch sports tourism (event sports tourism) or to venerate attractions associated with the physical attractions (nostalgia sport tourism)
To remember :
- Active Sports Tourism - someone who travels to a destination to participate, officiate, or assist in the production of a specific sport event or activity
- Event Sports Tourism - someone who travels to a destination for spectator purposes
- Nostalgia Sports Tourism - someone who travels to a destination or attraction to reminisce, appreciate or educate themselves about a particular sport
To remember :
Five Areas of Sport Tourism:
- Resorts
- Cruises
- Attractions
- Tours
- Events
Additional Types of Tourism
Adventure Tourism: travelling with a specific purpose to actively participate in and explore a new experience, generally one that is more extreme or active and involves a high level of perceived risk and controlled danger for the participant
Cultural Tourism: individual experiences enjoyed at a destination. Homestay tourism is a form of tourism where the tourist will immerse themselves in a particular culture, by living with ordinary people at their destinations for a period of time.
Cruise Tourism: involves tourists staying on a ship for a certain period of time, depending on the distance travelled
Medical and Health Tourism: Medical tourism refers to people traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who travelled from less-developed countries to major medical centres in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable at home.
Nostalgia Tourism: traveller visits a destination that holds sentimental value
Shopping Tourism: the primary focus for the undertaking the journey is shopping, no matter which product is purchased
Urban Tourism: the act of travelling to cities for the purpose of tourism. The major attractions for tourists to these cities include festivals, waterfront developments, historical districts, shopping centres and convention centres
Volunteer Tourism (volunteerism): individuals travel to a destination and engage
Significance of Tourism
- Tourism is a discretionary activity = if you don’t have money, you can’t travel
- Tourism has implications on the global growing economy
- Technological advancements have made researching and booking holidays and travel related products easy to reach
- Global travel has become more accessible for all classes of people in the developed world
Features of the Tourism Industry
Complexity
- includes several fields of activity
Fragmented
- many companies compete; there is no single or small group of companies which dominate the industry
Diverse
Volatility
High Fixed Costs
Vulnerability
Resilience
Tourism as a Product
To remember :
Tourism is an intangible and unpredictable product - you have to go to the destination and then the experience begins.
Nature of Tourism as a Product
Inflexibility
- Inflexibility can be seen when the seating capacity in a transport facility, hotel rooms is fixed, and it is impossible to meet the sudden demand during seasons. At the same time during off seasons the demand is less and capacity remains unutilized
Perishable
- The service provided by the tourist industry is highly perishable. For example: an unused hotel bed or a vacant seat in an aeroplane leads to non utilisation of capacity.
Intangible
- Tourism is an intangible product means tourism is such kind of product which can not be touched or seen and there is no transfer of ownership, but the facilities are available for specified time and for a specified use.
Inseparable
- Tourism products are provided and consumed at the same time. This is unlike most products which are manufactured first and then resold to the consumer
Fixed Location
- The destinations are fixed and efforts are required to make the potential tourists to visit the location.
Large Financial Investment
- Modern tourist establishment requires large financial investment both to start and to maintain the services making it highly risky as the rate of return is critically important.
The Primary Industries Involved in Tourism (umbrella)
- Accommodation and catering - place where tourists will stay for the night while at a destination, depending on their interest and budget
- Attractions - primary reasons why tourists visit a destination. Anything that draws the tourist's attention
- Entertainment - incorporates recreational activities and facilities that the tourists undertakes during their free time
- Transportation - tourism industry would not exist without transport
- Services - travel agencies, visas, etc
All of the above are service orientated industry and these type of industries have unique characteristics towards their products.
The Secondary Factors Influencing and Being Influenced by Tourism
Competition, crime, politics, etc
Definitions
The Difference between Normal Products and Tourism as a Product (Characteristics of Tourism as a Product)
- Limited Supply - facilities/ disposable income
- Instability of Demand - seasonal changes/ what tourists are looking to see
- Elasticity of Demand - being able to bounce back from challenges or obstacles
- Seasonality of Demand - only being able to function during specific seasons
- Competition - Competitions Act/ competitor prices
- Distribution - advertising - you have to go to the place
- Intangibility - sell the experience, not the place
- Consumption and Production - occur at the same time, sell the experience
- Standardisation - setting standards across the board that are followed through
- Fixed Location - cannot move the attraction
- Perishables - trends set by or for people
- Financial Investments - need capital to start and maintain services, difficult to get bank loans
The Tourism System
- Created by Neil Leiper in 1979- adapted in 1990
- Tourism as a system functioned under various environments:
- Eg. Human, Socio, Cultural, Economical, Technological, Physical, Political & Legal Environment.
- Leipers Model:
- The Tourist (human element)
- Geographical Elements
- The Tourism Industry
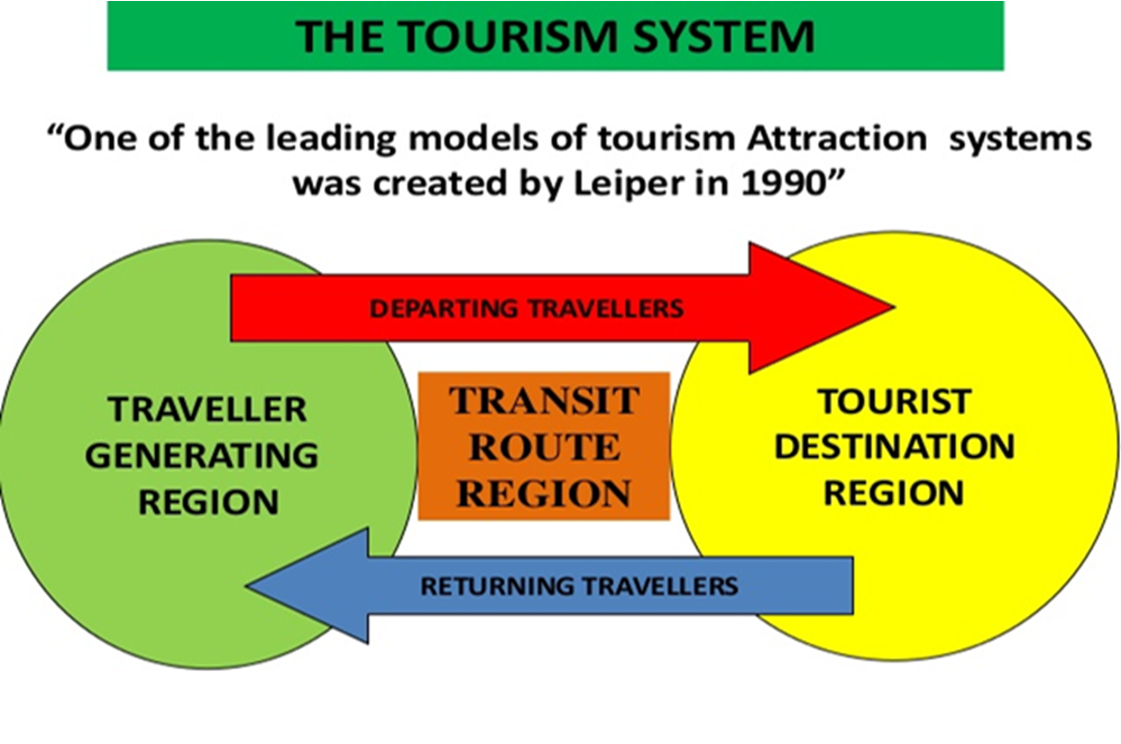
Geographical Elements in Leiper's System
- Traveller Generating regions: permanent residential bases of the tourist, this is the location of the basic market of the tourist industry; tourists possesses
- Push factors.
- Transit Route regions: paths that link the tourist generating regions to the tourist destination region.
- Tourist Destination regions: locations which attract tourists to stay temporarily. These function as Pull factors.
- ‘Push’ factors are the intangible desires that are generated from within the person. These factors encourage individuals to move away from their home setting through Tourism
- ‘Pull’ factors are external travel stimulants. These are attributes of a different place which attract or 'pull' them towards visiting it.
The Tourism Industry in Leiper's System
The Tourism Industry is the combination of different industries:
- Travel Agencies
- Hotels
- Transportation services
In the traveller-generating region, we can find travel agents and tour operators. In the destination region, we can find attractions and hospitality industry, in the transit route region, we have the transport sector.
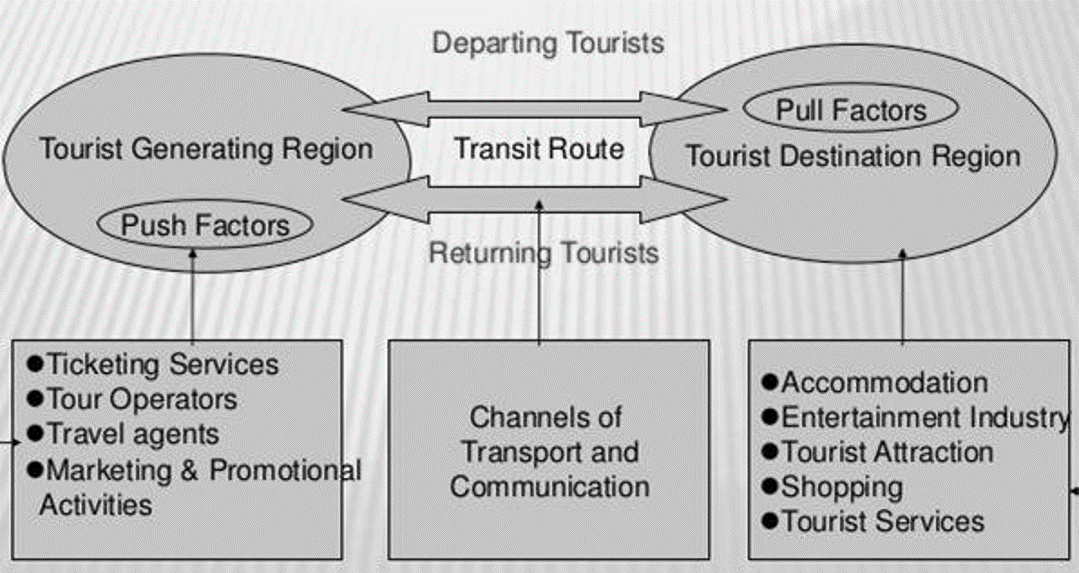
To remember :
The following are the five primary elements that complete the tourism system:
- At least one TOURIST
- At least one TOURIST GENERATING REGION
- At least one TRANSIT ROUTE REGION
- At least one TOURIST DESTINATION REGION
- A travel and TOURISM INDUSTRY

