There are 2 methods of reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction
There are 2 methods of reproduction
Asexual reproduction takes place by 6 different methods:
FISSION
In the process of fission, a unicellular organism splits to form 2 or more new organisms
There are 2 types of fission
BINARY FISSION
Binary fission
Amoeba
Amoeba reproduces by binary fission by dividing its body into two parts
In this way, one parent amoeba divides to form two smaller amoebae.
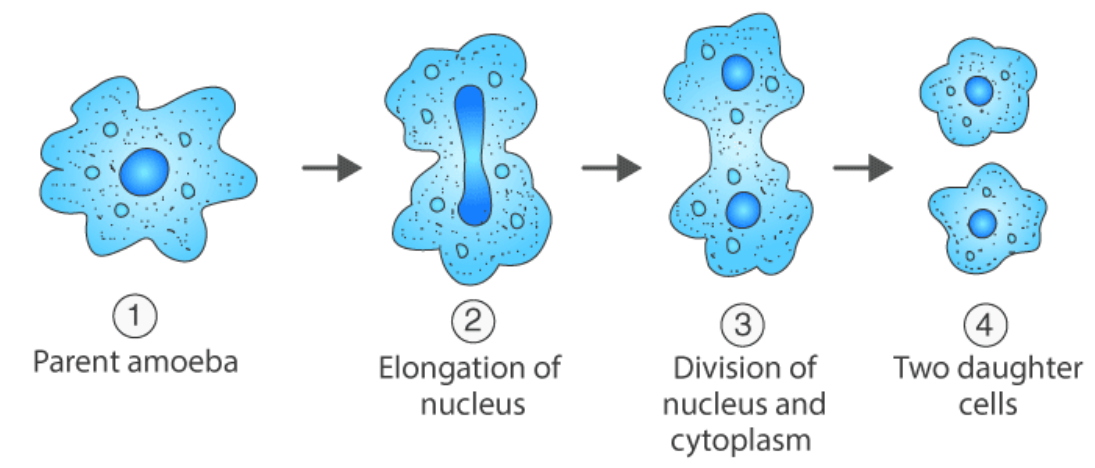
Amoeba reproducing by binary fission
Paramecium
Paramecium is a unicellular animal having short thread like structures called cilia over its surface.
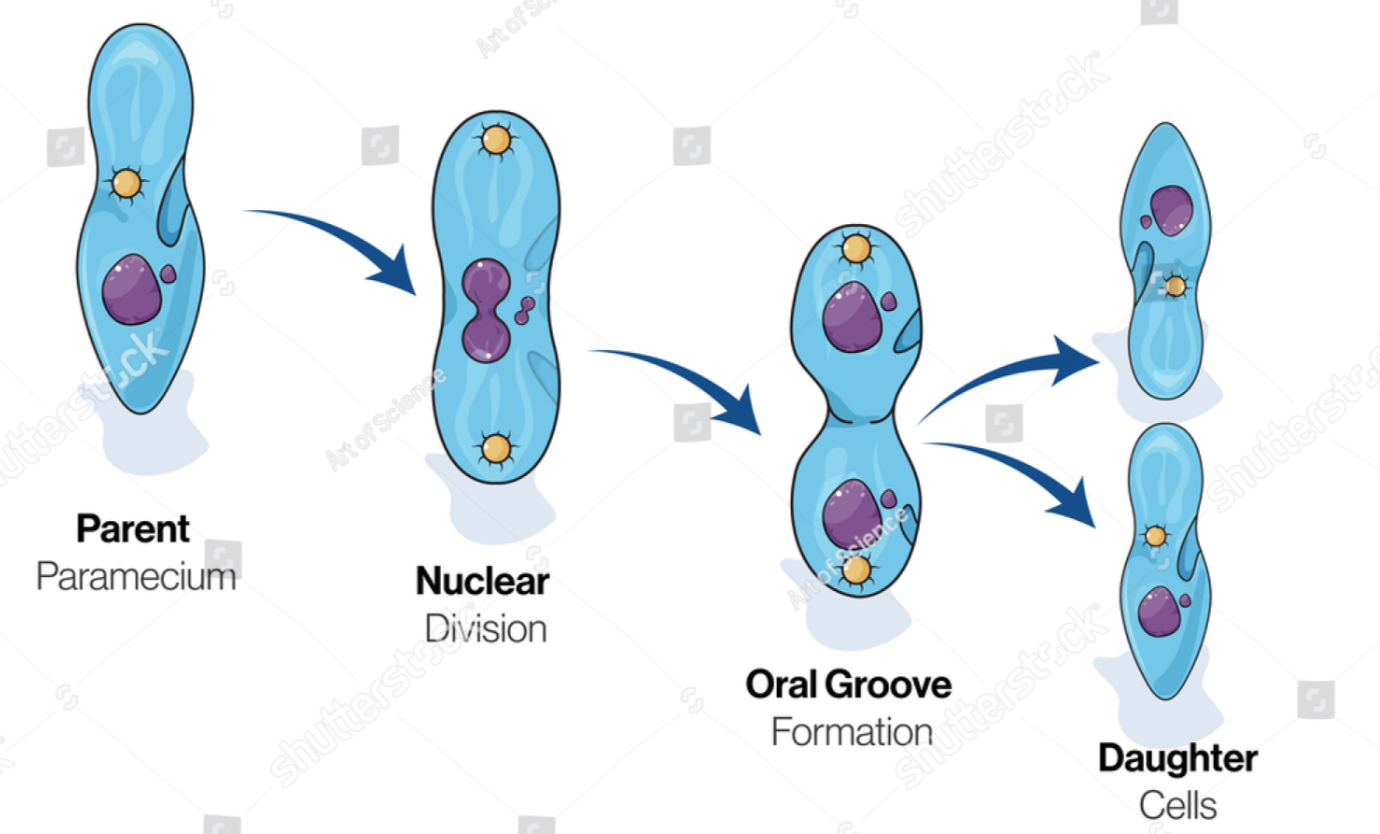
Binary fission of paramecium
Leishmania
Leishmania is a unicellular animal (which is a protozoan).
Leishmania has a greater degree of organization in its body, having a whip-like structure called flagellum.
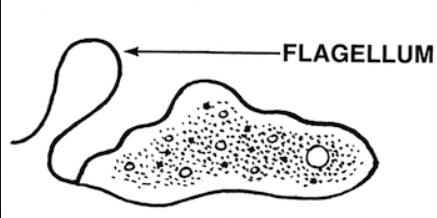
Flagellum
Leishmania
MULTIPLE FISSION
Plasmodium
Plasmodium is a protozoan which reproduces by the asexual method of multiple fission.
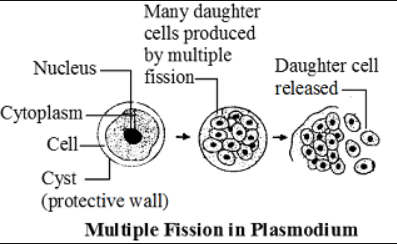
Multiple fission in plasmodium
BUDDING
Hydra
Hydra is a simple multicellular animal. Hydra reproduces by the process of budding.
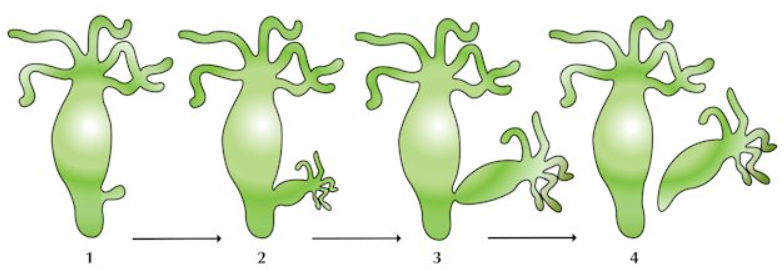
Budding of hydra
Yeast
Yeast is a tiny, unicellular, non-green plant (which is a fungus).
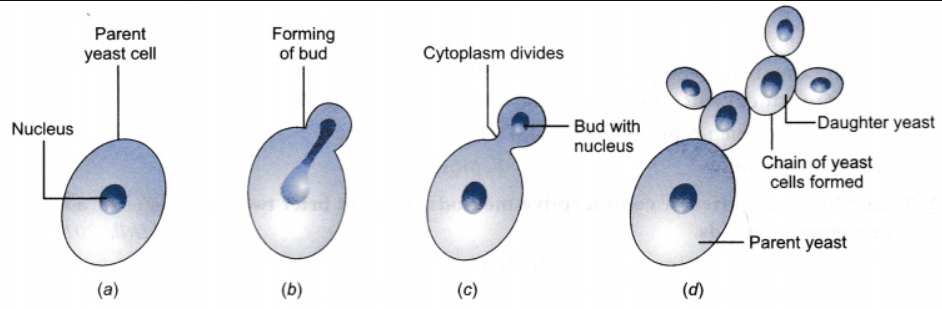
Yeast reproducing by budding
SPORE FORMATION
Rhizopus
REGENERATION
Planaria.
Planaria is a flatworm which is found in freshwater ponds and slow moving streams.
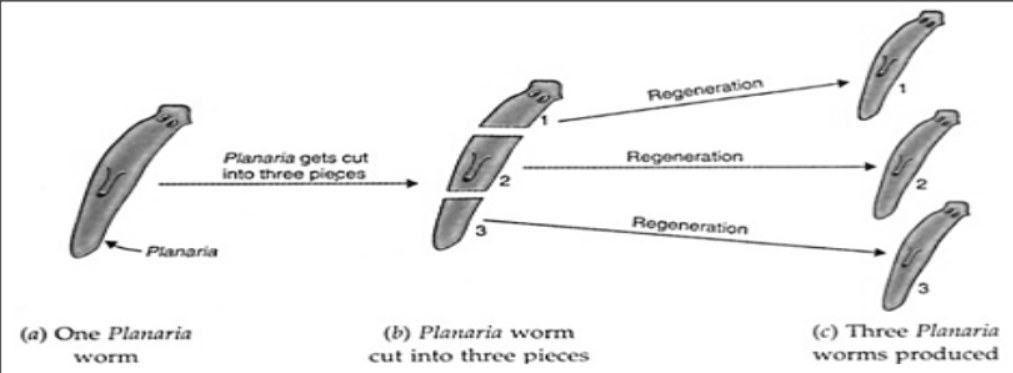
Regeneration in Planaria
The regeneration of an organism from its cut body part occurs by the process of growth and development.
FRAGMENTATION
Spirogyra
Spirogyra is a green, filamentous algae plant which is found in ponds, lakes and slow moving streams.
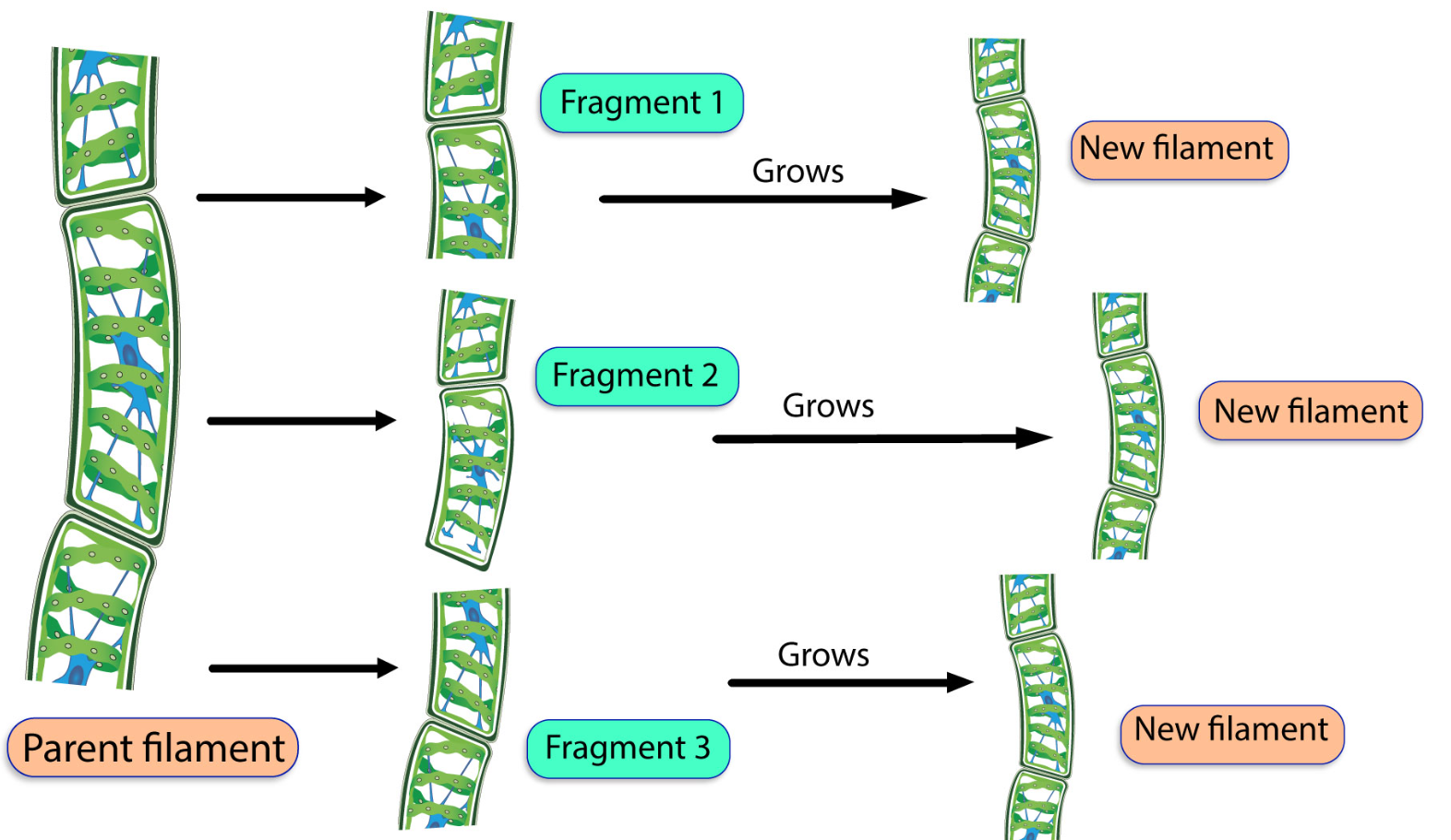
Reproduction of spirogyra by fragmentation
The main difference between fission and fragmentation is that in fission a unicellular organism breaks up to form 2 or more daughter organisms, whereas in fragmentation, a multicellular organism breaks up to form two or more daughter organisms.
VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION
Bryophyllum
Buds are present on the stems as well as the leaves of the bryophyllum plant which can develop into new plants.
Money Plant
The tuber has a number of buds (called eyes). each bud of the tuber grows into a new plant when the old tuber is planted in the soil in the next growing season.
There are 2 types of tubers:
Potato
potato tuber is an underground stem of the potato plant.
ARTIFICIAL PROPAGATION OF PLANTS
There are 3 common methods of artificial propagation:
CUTTINGS
LAYERING
Plants like strawberry and raspberry are propagated by the natural layering method.
GRAFTING
TISSUE CULTURE
The process of tissue culture for producing new plants:
The tissue culture technique is being used increasingly for the production of ornamental plants like orchids, dahlia, carnation, chrysanthemum etc. the production of plants by the method of tissue culture as micropropagation.
DO ORGANISMS CREATE EXACT COPIES OF THEMSELVES IN ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Asexual reproduction usually results in the production of genetically identical offsprings, the only genetic variation arises as a result of occasional inaccuracies in DNA replication at the time of cell division.
There are 2 methods of reproduction
Asexual reproduction takes place by 6 different methods:
FISSION
In the process of fission, a unicellular organism splits to form 2 or more new organisms
There are 2 types of fission
BINARY FISSION
Binary fission
Amoeba
Amoeba reproduces by binary fission by dividing its body into two parts
In this way, one parent amoeba divides to form two smaller amoebae.

Amoeba reproducing by binary fission
Paramecium
Paramecium is a unicellular animal having short thread like structures called cilia over its surface.

Binary fission of paramecium
Leishmania
Leishmania is a unicellular animal (which is a protozoan).
Leishmania has a greater degree of organization in its body, having a whip-like structure called flagellum.

Flagellum
Leishmania
MULTIPLE FISSION
Plasmodium
Plasmodium is a protozoan which reproduces by the asexual method of multiple fission.

Multiple fission in plasmodium
BUDDING
Hydra
Hydra is a simple multicellular animal. Hydra reproduces by the process of budding.

Budding of hydra
Yeast
Yeast is a tiny, unicellular, non-green plant (which is a fungus).

Yeast reproducing by budding
SPORE FORMATION
Rhizopus
REGENERATION
Planaria.
Planaria is a flatworm which is found in freshwater ponds and slow moving streams.

Regeneration in Planaria
The regeneration of an organism from its cut body part occurs by the process of growth and development.
FRAGMENTATION
Spirogyra
Spirogyra is a green, filamentous algae plant which is found in ponds, lakes and slow moving streams.

Reproduction of spirogyra by fragmentation
The main difference between fission and fragmentation is that in fission a unicellular organism breaks up to form 2 or more daughter organisms, whereas in fragmentation, a multicellular organism breaks up to form two or more daughter organisms.
VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION
Bryophyllum
Buds are present on the stems as well as the leaves of the bryophyllum plant which can develop into new plants.
Money Plant
The tuber has a number of buds (called eyes). each bud of the tuber grows into a new plant when the old tuber is planted in the soil in the next growing season.
There are 2 types of tubers:
Potato
potato tuber is an underground stem of the potato plant.
ARTIFICIAL PROPAGATION OF PLANTS
There are 3 common methods of artificial propagation:
CUTTINGS
LAYERING
Plants like strawberry and raspberry are propagated by the natural layering method.
GRAFTING
TISSUE CULTURE
The process of tissue culture for producing new plants:
The tissue culture technique is being used increasingly for the production of ornamental plants like orchids, dahlia, carnation, chrysanthemum etc. the production of plants by the method of tissue culture as micropropagation.
DO ORGANISMS CREATE EXACT COPIES OF THEMSELVES IN ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Asexual reproduction usually results in the production of genetically identical offsprings, the only genetic variation arises as a result of occasional inaccuracies in DNA replication at the time of cell division.