A Safety Management System (SMS) is a systematic approach to managing safety, including organizational structures, responsibilities, policies, and procedures.
Legal basis: EU Regulation 2017/373.
A Safety Management System (SMS) is a systematic approach to managing safety, including organizational structures, responsibilities, policies, and procedures.
Legal basis: EU Regulation 2017/373.
To prevent incidents by building and maintaining a strong safety culture.
Everyone is responsible for safety.
All staff should report any safety concerns.
Encourages a Just Culture: mistakes can be reported without fear of punishment.
Used to document and analyze technical incidents within the SMS framework.
Defined as a combination of:
ATSEPs play a key role in managing changes and ensuring safety through:
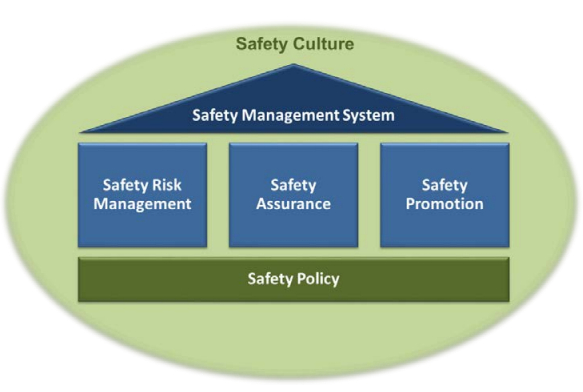
Q: What are the components of an SMS?
A: Policy, Risk Management, Assurance, Promotion.
Q: What is the purpose of risk management?
A: Identify, assess, manage, and mitigate risks to reach acceptable levels.
Q: Why are safety cases and requirements needed?
A: To ensure changes to systems are safe and documented, with clear goals and controls.
A Safety Management System (SMS) is a systematic approach to managing safety, including organizational structures, responsibilities, policies, and procedures.
Legal basis: EU Regulation 2017/373.

To prevent incidents by building and maintaining a strong safety culture.
Everyone is responsible for safety.
All staff should report any safety concerns.
Encourages a Just Culture: mistakes can be reported without fear of punishment.
Used to document and analyze technical incidents within the SMS framework.
Defined as a combination of:
ATSEPs play a key role in managing changes and ensuring safety through:
Q: What are the components of an SMS?
A: Policy, Risk Management, Assurance, Promotion.
Q: What is the purpose of risk management?
A: Identify, assess, manage, and mitigate risks to reach acceptable levels.
Q: Why are safety cases and requirements needed?
A: To ensure changes to systems are safe and documented, with clear goals and controls.