- Provide users with available capacity efficiently.
- Avoid overloads in the European ATM network.
- Prioritize safety, even if it means delaying traffic.
Définition
ATFCM
ATFCM is a critical process within Air Traffic Management (ATM) aimed at ensuring safety and efficiency in European airspace by balancing traffic demand with available capacity.
A retenir :
First priority = SAFETY
Objectives
Key Players
- ANSPs (Air Navigation Service Providers): Manage airspace and provide capacity.
- Airspace Users: Submit and update flight plans.
- Handling Agents: Provide real-time flight status updates.
- Airspace Management Authorities: Coordinate civil and military needs.
- Airports: Ensure infrastructure readiness and coordination.
NMOC (Network Management Operations Centre)
- Formerly known as CFMU.
- Central hub for managing European air traffic flow.
- Tasks include:
- Managing the ATFCM network.
- Developing strategies and route efficiency.
- Balancing demand and capacity.
- Processing flight plans (FPLs).
ATFM Area
- Only flights within or entering the ATFM area are subject to flow restrictions.
- Flights outside this area are not regulated.
How ATFCM Works
- Traffic Forecasting: Based on flight plans processed by IFPS.
- 4D Profiles: Created to predict aircraft trajectories.
- Sector Load Calculation: Determines which sectors are affected and their capacity.
- Capacity Definition: Based on simulations and operational evaluations.
- Flow Monitoring Positions (FMPs): Monitor and act on traffic predictions.
Slot Allocation
- CTOT (Calculated Take-Off Time): Issued when regulations are applied.
- ETOT (Estimated Take-Off Time): Used for traffic prediction.
- Principles:
- First come, first served.
- Delay distributed among all flights.
- Late filers are treated differently.
CTOT = EOBT + TT (Taxi Time) + Delay
A retenir :
Airport slot != ATC slot : ATC slot overrules Airport slot.
FMP Zurich
Définition
FMP
Flow Management Position
- Acts as a liaison between local ATC and NMOC.
- Monitors traffic, optimizes flow, and manages ATC slots.
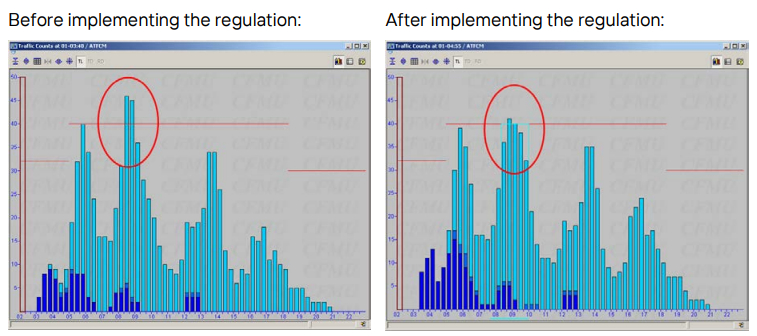
- Sector configurations are planned based on staffing, weather, and traffic.
Each sector has a capacity per hour.
eg : M1 is 44 FPL max which is only 75% of the max capacity in case of emergencies to handle.
Flight profile is stored in NMOC database
- Point profile : profile by waypoint
- Airspace profile : profile by sectors. Usefull to calculate demand on each sector and adjust the capacity

